Ever wondered how Netflix keeps working when millions of people press play at the same time?
A huge reason for this is the fact that they use serverless architecture to run certain parts of the platform.
It’s a computing approach that allows Netflix to handle global demand in terms of streaming in a highly efficient manner.
This level of reliability at a global scale is what makes serverless worth paying attention to for other businesses, too.
In this article, we will learn all about serverless architecture, its benefits, limitations, and everything you need to know before using it for web development and other applications.
By the way, if you’re curious about web development tactics that still work wonders today, we’ve got you covered.
Our updated blog Web Development Tactics breaks it all down.
Feel free to check it out whenever you’re in the mood to level up
What Is Serverless Architecture?
Serverless architecture is an approach where developers can write code for applications and upload it to the cloud provider’s platform. They focus purely on running code while leaving it up to the provider to manage all the underlying tasks like server setup, maintenance as well as scaling.
The developer writes the “what” (image resizing code), and the FaaS platform handles the “how” (servers, scaling, execution), responding to events like file uploads, API calls, or database changes.
According the Grand View Research, the serverless computing market is projected to reach USD 52.13 billion by 2030. So, if you are considering a faster, more affordable and innovative approach to app development, serverless is a good choice.
How Serverless Architecture Works
As you can see, the process of serverless architecture typically involves a three-step flow:
At first, the application logic is uploaded to a cloud platform. This is the part that handles actions like processing a request, saving data, or sending a response.
Next, you decide what should trigger that logic. It could be a user clicking a button, submitting a form, calling an API, or uploading a file.
Finally, when that trigger happens, the cloud provider runs the code automatically. When the task finishes, it stops. Nothing runs in the background unless another action occurs.
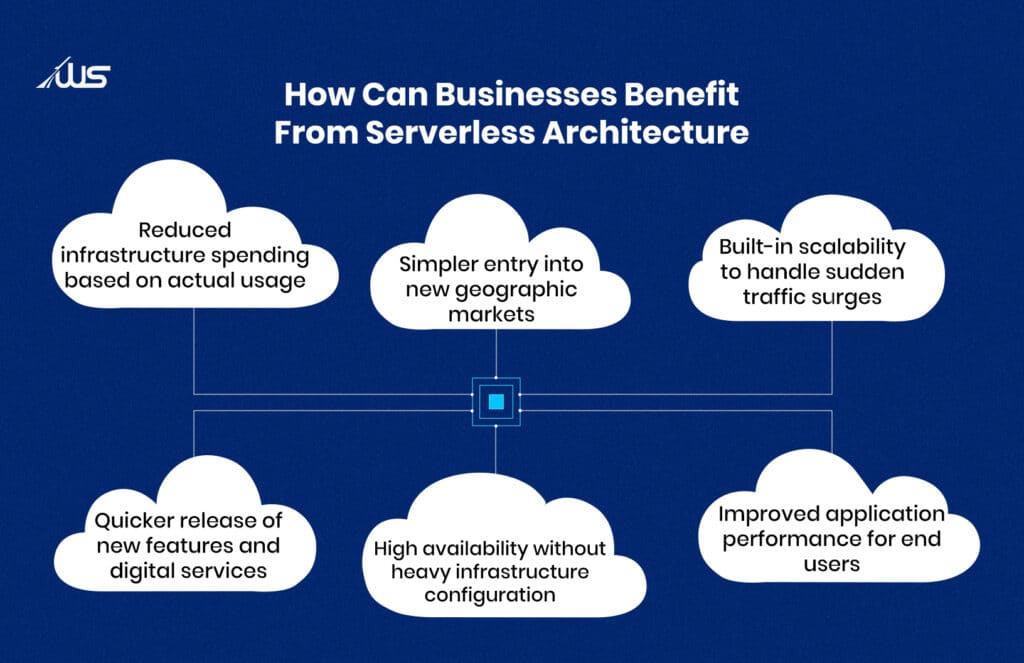
Key Benefits of Serverless Architecture for Businesses
There are some very obvious benefits of opting for serverless architecture, like cost efficiency and much faster development duration. Those of you who are considering the serverless development model to develop your app can have a look at exactly what they can expect and the ongoing value it brings.
1. Lower infrastructure costs with flexible usage
When your application runs on a traditional setup, you are paying for the full capacity whether people use it or not.
But, with serverless, there would not be fixed spending.
Basically, you pay when your application actually does something. So, if usage slows down, your costs slow down too. If activity picks up for a short period, you only pay for that window. For many businesses, this removes the pressure of guessing future demand. Your monthly bills tend to reflect real usage instead of assumptions you had to make in advance.
2. Automatic scaling during traffic spikes
App traffic does not grow in neat patterns. It tends to jump and drop depending on a range of different factors.
Taking this into consideration, serverless systems are designed to handle fluctuations automatically, both when usage increases and when demand falls.
From your side, there is nothing to tune or monitor constantly. This is obviously useful, and particularly so when launches and promotions drive short bursts of activity.
3. Faster launch of new features and services
When you decide to add a new app feature, you would typically require it to be built to fulfil specific actions or workflows. You wouldn’t want to overhaul the entire system.
Serverless makes it easier to release small updates, test them, and adjust based on how users respond.
For businesses, this often means shorter release cycles and fewer internal blockers. The focus stays on what the feature does, not what needs to be provisioned to support it.
4. High availability without complex setup
Many businesses need their applications to be kept available around the clock. And, this usually requires careful planning and ongoing oversight.
To ensure that that responsibility shifts away from you, serverless can be used.
The platform is designed to run across multiple locations and handle failures automatically.
This way, if one part slows down or stops responding, requests are routed elsewhere. Your application remains continuously reachable as a third-party (not you) has the job of keeping it online.
5. Easier expansion into new markets
A lot of the time, when a business expands to a new region, the infrastructure planning can slow systems down.
There is a need for them to operate across many geographic locations.
If your application is running on a serverless platform can, it run closer to users without building new systems from scratch.
You do not need to rethink architecture each time you expand.
The technical adjustments are done in the background while you focus on whether the market response is what you expected or not.
6. Better performance for end users
A sudden surge of traffic on your application would understandably cause performance issues. With serverless, responses are only triggered when users interact with your product.
Usually, the result is faster handling during busy periods because the system is not restricted by a fixed capacity.
App users do not experience lag even at times when traffic increases unexpectedly. From the user’s perspective, the app functions in a stable and responsive manner.
When an app behaves as it should (i.e., maintaining top performance), end users will continue to use it rather than go to your competitors in frustration.
Now, that you know the advantages that serverless architecture offers businesses, it’s important that you know that differences between serverless architecture vs. traditional systems.
Serverless Architecture vs Traditional Server-Based Systems
The choice of serverless architecture vs traditional server systems comes down to your specific business needs. In case your business involves unpredictable traffic, event-driven tasks, it would make sense to opt for serverless.
On the other hand, if your business has unpredictable yet high-volume traffic and/or low-latency needs (requires real-time response), then traditional server systems would be the better choice.
Let’s go through a few of the differences between Traditional and Serverless Architecture.
- Cost structure
Traditional systems are usually designed for planned capacity. Accordingly, you pay for servers, storage, and maintenance whether usage is steady or uneven.
Serverless works differently.
Costs are based on actions such as requests, execution time, or events. That means spending rises and falls with activity. You get a significant advantage, as things shift from fixed infrastructure costs to usage-based costs.
It is not always cheaper, but it makes it easier for business owners to trace costs back to actual application activity.
- Scalability and flexibility
A Capgemini study says that 77% of executives agree that the scalability and performance of cloud services is central to business growth and competitive differentiation.
Business owners tend to add app capacity before they need it and hope demand matches their expectations.
Serverless removes the need for planning.
The system scales automatically as per the usage. You wouldn’t need to pre-plan when to add or remove resources.
Your app works smoothly and flexibly when traffic patterns are unclear or change frequently.
This works best for businesses that have products that evolve quickly or ones that experience irregular growth. They are not forced to make constant infrastructure adjustments.
- Long-term maintenance
Maintaining traditional systems often involves regular updates, monitoring, and capacity. Serverless reduces that surface area.
To maintain traditional systems you need to regularly review the app updates and capacity.
This is not the case when you use serverless, as the provider is the one managing servers, operating systems and even patch schedules.
Your internal team would not have to put in effort to keep the infrastructure running; they would just have to concentrate on keeping the application logic flawless.
What is the Difference between Microservices and Serverless Architecture?
Microservices is the approach of software development where developers structure an entire application as several small, interconnected yet independent parts. Each of these services is loosely coupled and is responsible for specific business functions.
Like the serverless model, microservices too have the goal of offering sufficient adaptability and flexibility when it comes to building intricate applications.
As mentioned earlier, serverless architecture allows developers to build and run app code without needing to manage servers. That is not to say servers are not involved, because they certainly are. But in this approach, the underlying architecture is outsourced to a cloud provider.
If your business logic involves a good amount of APIs and event-driven tasks, such as order processing (ecommerce) or stock alerts (financial trading), and so on, you can benefit from the serverless approach to software development.
Limitations of Serverless Architecture to Be Aware Of
Before adopting serverless architecture, you need to make sure you are choosing it only if your business workloads require such a model. For this, you need to be familiar with the limitations of this technology to know the hurdles you may face so that you can address them from the start.
Less direct control over infrastructure
If you have chosen to use serverless, you are dependent on a third-party to fine-tune servers and control where every app process runs.
You are trusting the provider to handle decisions that were previously internal.
This works ideally when your app workloads match the capabilities of the serverless platform you have picked.
Performance delays in certain scenarios
Serverless architecture does not behave the same way in every situation.
So, if there is a function that is triggered after being idle, there can be a short delay before it responds. In many applications, users never notice this. In others, especially those requiring immediate response, it can matter. This is not a constant issue, but it is something businesses need to be aware of.
Dependency on cloud service providers
As you have realised, using serverless links your application closely to the cloud platform offering it.
Now each provider is bound to have their own services, limitations, and pricing models.
If you decide to switch to another provider later, it can take time and effort. This is not always a drawback, but it is something to think about early.
While you gain simplicity, speed, and the ability to scale instantly, you also accept that moving the system elsewhere won’t always be straightforward. And as you explore broader Cloud/AI transformations, you’ll see how these choices impact what comes next, especially with 8 game‑changing ways AI is set to transform web development, a topic we’ve already broken down for you.
Not ideal for every type of workload
Those applications that are driven by events, requests, or background tasks are the ones that work best on serverless architecture.
If your app involves long-running processes or systems requiring constant low-latency execution, this model might be less suitable.
As a business owner, you need to check if serverless aligns with how your application actually behaves rather than forcing a fit.
Common Business Use Cases for Serverless Architecture
Airbnb, Slack, and Coca-Cola, BMW, and Figma are just few of the top companies that take advantage of the serverless model for their systems.
While serverless architecture is designed to enhance business agility and operational performance, it is also an investment that decision makers need to evaluate thoroughly.
If you need to figure out whether this cloud model suits your business needs, you can look at the top use cases of serverless architecture.
Customer-facing web and mobile applications
If you have an app that requires users to interact with in short bursts, then you should consider serverless.
This means that user interactions like page loads, form submissions, and other app actions will trigger code only when a particular interaction takes place.
This keeps systems responsive without constant resource usage. This is especially helpful for customer-facing applications, as all unpredictable traffic can be smoothly handled without manual intervention.
E-commerce platforms and seasonal campaigns
In case you run an online store, you often see uneven demand driven by sales, promotions, or seasonal trends.
Suppose you are running a marketing campaign for your store, and the app activity increases.
Then, thanks to serverless architecture, the system will respond automatically to manage the increased activity.
This leaves your team free to focus on things like pricing, inventory, and customer experience.
APIs and backend services
In an app, an API is what connects systems and processes user requests.
So, since APIs are event-driven by design, serverless is a good choice for API-based apps.
Each request triggers a response and then stops. This keeps backend services lightweight and easier to scale.
Serverless APIs reduce the overhead of running always-on services. They respond when triggered and stay inactive when not in use.
Data processing and automation tasks
Looking at the basic functions of serverless architecture, it’s easy to see how well-suited it is for background work. These could be tasks like data transformation, file processing, or scheduled jobs.
Tasks like these usually run in response to specific events. A file upload, a database update, or a scheduled trigger starts the process.
Once finished, nothing continues running. This model keeps systems efficient and predictable.
Supports early-stage feedback with ease
In the early phase when your app is going through iterations and receives feedback, then serverless works best. This phase of uncertainty can be fully supported by the serverless model.
You can build features quickly, adjust them, or remove them without reworking infrastructure. Costs are only based on usage, which helps during early growth stages.
For startups testing ideas or launching minimum viable products, this reduces early commitment while still allowing scale if adoption increases.
Closing Thoughts
Looking at the breakthroughs in this technology, it’s clear that serverless architecture will continue to be relevant in the coming years. It changes how your product grows, how costs behave, and how much of your attention is spent on infrastructure instead of outcomes. For many businesses, that shift is the real value.
If you are planning to opt for serverless architecture to boost your app development, Webskitters Technology can take on your project. Our experts will support your business growth with cutting-edge app development services to help you outpace your competitors. So, let’s get started right away.
FAQs
What is a key benefit of serverless architecture?
The biggest benefit is you only pay when your application runs, so costs follow real usage and you avoid paying for servers that sit unused.
What is the difference between Microservices and Serverless architecture?
Microservices split an application into smaller services you manage. Serverless runs individual functions for you, with the cloud provider handling servers, scaling, and availability automatically.
When to use serverless architecture?
You should use serverless when your traffic changes often, tasks are event driven, and you want to launch features quickly without managing infrastructure yourself daily.
Does serverless architecture mean there are no servers?
No, servers are still used, but you do not manage them. The cloud provider runs, scales, patches, and maintains servers behind the scenes for you.


 December 29, 2025
December 29, 2025